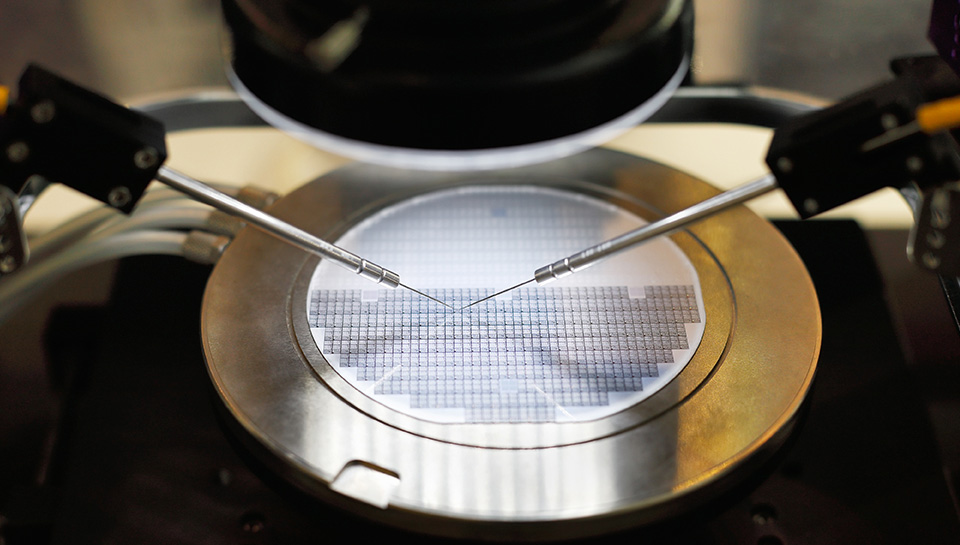
Laser Micromachining
Gateway Laser Services specializes in laser micromachining features on parts requiring micron-level precision for various electronic components including semiconductors. Our laser systems cleanly process unique materials used for electronics including most polymers/plastics, metals, and ceramics. Featured services include laser processing entire components such as deposition/shadow masks, laser drilling micro-holes for various vias, and laser cutting complex geometries on thin ceramics. We also have the ability to remove plastic materials from metal through laser ablation.
Benefits
Precision
Highly accurate, consistent micromachining with features down to .0002” (5µm) and tolerances down to +/- .00004” (1µm)
Quality
Exceptionally clean processing across most polymers/plastics, metals, and ceramics while maintaining the integrity of the material
Scalability
Quick turnarounds for prototype development or contract manufacturing services for full production parts
Featured Applications
Laser micromachining precise features on electronic components including:
- Semiconductors
- MEMS (Micro-Electromechanical Systems)
- Acceleration Grids
- Coils
- Contacts
- Micro-Washers, Gaskets, & Shims
- Plates & Stencils
- Sensors
- Shadow Masks & Deposition Masks
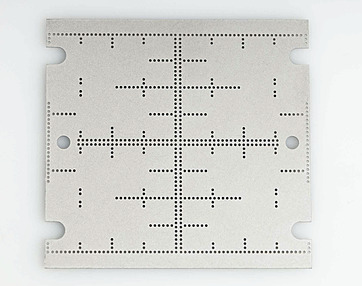
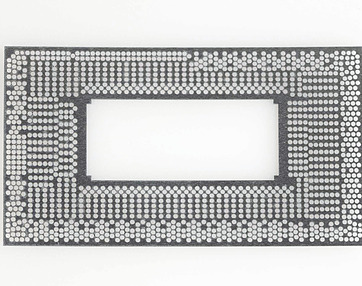
Our Work Examples
Click on image for additional information including feature size and material (please note parts are significantly magnified)